NoFollow Links in SEO
Auch verfügbar in Deutsch: NoFollow Links – wichtig für Ihre SEO?Table of Contents

Can NoFollow links hurt you? #
The value of NoFollow links has often led to heated debates among online marketers and SEOs. Ever since Google Penguin has been rolled out, the risk of links has become a central question.
People often claim that links marked as NoFollows have no impact. Some SEOs still rely on former Google statements suggesting that NoFollows do not pass PageRank, taking this as “evidence” that spammy NoFollow links cannot put you at risk of a Penalty.
Read on and learn:
- what Google has to say about NoFollow links
- what SEOs think about NoFollow links
- why it’s worth looking at NoFollow links
- how we treat NoFollow links in LinkResearchTools
Learn all about NoFollow 2.0, UGC and SPONSORED Link Attributes
What are NoFollow Links? #

A NoFollow tag is a way that allows webmasters to tell search engines “Don’t follow links on this page or Don’t follow this specific link. A link can have one or more rel attributes, where “rel” is short for “relationship”. These attributes help define the relationship a link has with a page that it points to.
A NoFollow link looks like this:
<a href="http://www.example.com/" rel="nofollow">Anchor Text</a>
Nofollow links are often used in blog or forum comments in an attempt to take away the incentive for automatic link spammers to place their links there.
Interestingly enough, however, this has hardly reduced comment spamming.
Well, guess why!
Debates and opinions on the effects and risks of NoFollow links #
The debate on NoFollows is often focused on the following questions:
Do NoFollow links affect rankings in search results and how does Google evaluate them? #
Let’s look at a practical case. A link from Wikipedia is more relevant as to traffic and thus more important for SEO even if the link is marked as nofollow. Some people believe that NoFollow links pass Trust. However, this could also imply that negative Trust could be passed as a spam signal.
Can a high amount of low-quality NoFollow links in your backlink profile put your website at risk? #
If your website was affected by a Google Penalty, you need to focus on the links you bought in the past and on the spam examples provided by Google. But what if there were NoFollow links among those bad, manipulative links named by Google?
Should NoFollow links be disavowed? #
Many SEOs and consultants believe that disavowing a link will simply turn it into a nofollow. This would imply that there is no point in disavowing a NoFollow link. But what if it’s precisely those NoFollow links that are causing problems? The statement that disavowed links are “merely” turned into NoFollow links was a casual remark from Google when they gave an explanation of the Disavow Tool. However, this would mean that harmful NoFollow links cannot be made ineffective through disavowing.
Should you bother with NoFollow links at all or are they completely meaningless? #
From the above-mentioned presumptions, one could think that there is no need to deal with NoFollow links as they don’t imply any risk. If, however, we assume that Google’s explanation is a simplification, on the one hand, and inconsistent, on the other, investing more time in the analysis and review of NoFollow links is worthwhile.
Google’s statements on NoFollows #
How does Google handle NoFollow links? #
In general, we don’t follow them. This means that Google does not transfer PageRank or anchor text across these links. Essentially, using NoFollow causes us to drop the target links from our overall graph of the web.
However, the target pages may still appear in our index if other sites link to them without using NoFollow, or if the URLs are submitted to Google in a Sitemap. Also, it’s important to note that other search engines may handle NoFollow in slightly different ways.”
Source: Google Support
On September 9, 2013 - Matt Cutts said that
typically, NoFollow links cannot hurt your site.
The fact that he used the word “typically” is an indication that NoFollow links can hurt your website in exceptional cases.
Statements from the Google spam team concerning 4,649 spam links examples #
The evaluation of the answers from the Google spam team makes things even more interesting. In 2013, Google began to provide spam link examples as part of their answers in Reconsideration Requests. A total of 4,649 spam link examples for 854 domains could be collected from the period between August 16, 2013, and July 2, 2014. Precisely these links named by Google were checked with the Link Check Tool (LCT) to measure the status of the links as of July 2, 2014.
Spam links named by Google sorted by their link status #
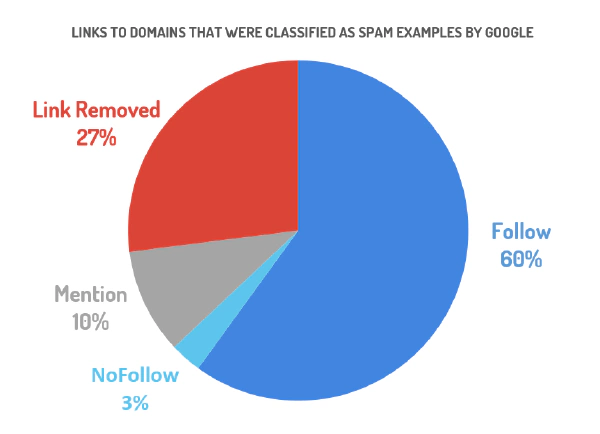 Spam links named by Google sorted by their link status
Spam links named by Google sorted by their link status
The result shows that already 27% of the links had already been removed and that 10% of the links have been turned into mentions in the meantime (meaning a domain is mentioned but not linked). About 3% of the spam links named by Google were NoFollow links, some of which have existed on article directories or press portals for years.
Below, Google provides two examples of links. The first link is an article directory that has been taken offline in the meantime. The second link leads to the relatively known press release PRNewswire.com.
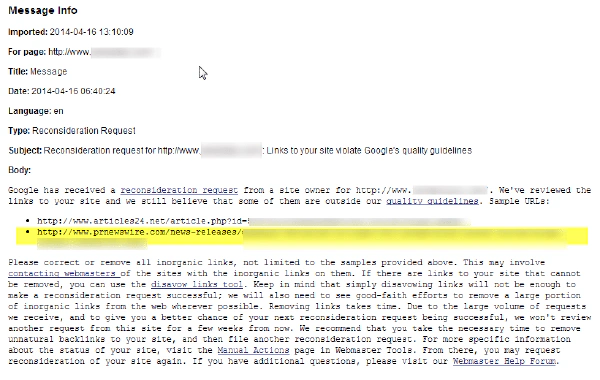 A typical rejection of a reconsideration request from Google
A typical rejection of a reconsideration request from Google
It takes an SEO’s trained eye to recognize that such a “press release” is simply a piece of text stuffed with Money Keywords that has obviously only been created for SEO purposes. Online press portals have been promoting the SEO value of their publications for years, and the domain PRNEWSWIRE.COM is relatively large – but there were other providers that had e.g. no hesitation in packing their clients against thousands of articles per day on relatively useless, article-stuffed domains, taking good money of course. And things were even more extreme on “free press portals”.
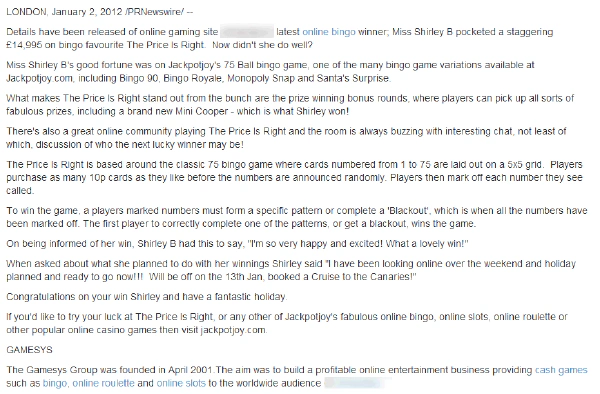 SEO press release with keyword stuffing with Money-Keywords as commonly used for years
SEO press release with keyword stuffing with Money-Keywords as commonly used for years
This example is especially interesting because the link was a normal Follow link first and changed to a NoFollow in July 2013 only after Google announced link spamming via press portals as a violation of their guidelines. PRNewswire took action quite quickly, but many other providers reacted to the change much later. Further analysis of such cases needs to be done, but it seems obvious that the current status of an existing link does not necessarily reflect its effect on Google Penalties.
The true intention of Google #
Google wants to make webmasters aware of their manipulation “attempts”, punishing the approach, not the links. And it does not seem absolutely necessary that the links are marked as Follow links. At least in some cases, it didn’t matter that links which were used massively for spamming before were changed to a NoFollow status.
How the SEO community sees NoFollow Links #
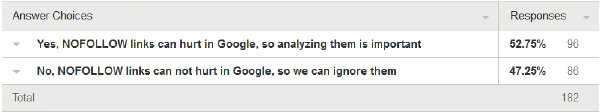
In July 2014 we started an open poll asking, among other questions, whether the participants believed that NoFollows can put a website’s ranking at risk or not. Slightly more than 50% of the 181 participants believed that NoFollow links can have a negative impact on their results in Google.
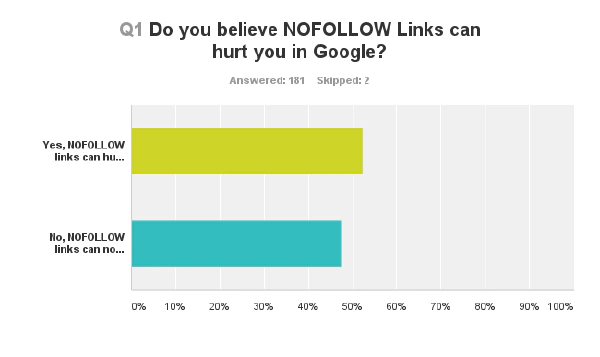 Webmasters were polled if they believe if NoFollow links can hurt them in Google were undecisive
Webmasters were polled if they believe if NoFollow links can hurt them in Google were undecisive
 Webmasters were polled if they believe if NoFollow links can hurt them in Google were undecisive
Webmasters were polled if they believe if NoFollow links can hurt them in Google were undecisive
The opinion of 181 participants whether NoFollow links can be risky or not.
How LinkResearchTools handles NoFollow Links #
Since 2014, LinkResearchTools (LRT) supports those two possible opinions when it comes to the risk of NoFollow links. Many users asked us for our opinion which analysis mode to use, and we always and still believe it’s very important to include NoFollow links in the analysis. Google included NoFollow links as spam examples as part of their answers to reconsideration requests.
The NoFollow evaluation is now pre-selected as the default option in Link Detox (DTOX), but you can always switch it back to ignore NoFollow links fully, also when reprocessing a report.
 NoFollow Links Evaluation Mode in Link Detox
NoFollow Links Evaluation Mode in Link Detox
The difference between a Link Detox report that has the NoFollow links evaluation activated and one that ignores NoFollow links can be major. You can see below a clear example of a Link Detox report that takes NoFollow links into consideration and one that doesn’t.
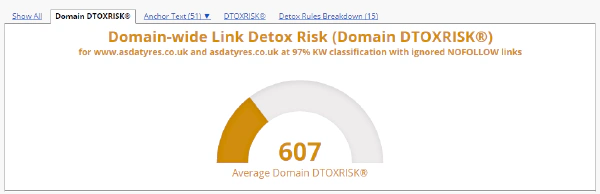 Link Detox Risk for a domain with ignored NoFollow links**Link Detox Risk for a domain with ignored NoFollow links
Link Detox Risk for a domain with ignored NoFollow links**Link Detox Risk for a domain with ignored NoFollow links
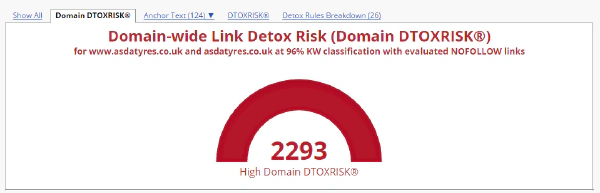 Link Detox Risk for a domain with evaluated NoFollow links
Link Detox Risk for a domain with evaluated NoFollow links
The domain-wide Link Detox Risk (DTOXRISK) is much higher when we choose to evaluate NoFollow links. You should remove or disavow all those NoFollow links that look spammy and have a high risk for your backlink profile. They influence the overall quality of your backlink profile. Only the fact that they are NoFollow links, does not make them risk-free.
Make sure that you have the right NoFollow link ratio in your niche #
Most websites have a mix of Follow and NoFollow backlinks. In some niches, it’s common to have a higher percentage of NoFollow links than in others. Using Competitive Landscape Analyzer (CLA) you can analyze your competitors and see the typical Follow / NoFollow link ratios of the domains that are ranking on the first page of Google for your industry.
You should aim to have similar NoFollow/Follow backlink ratios to your competitors.
There is no “golden rule” like a 20:80 ratio for NoFollow Links vs. Follow Links. Every industry, topic, keyword, language and country has different rules.
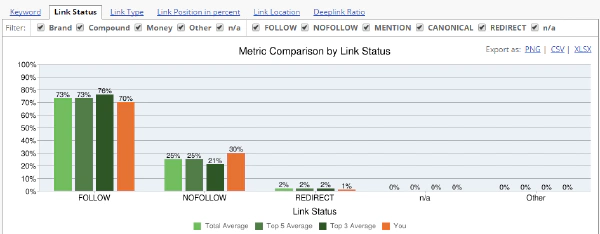 Competitive Landscape Analyzer CLA Link Status Ratio
Competitive Landscape Analyzer CLA Link Status Ratio
Conclusion #
 Analyze NoFollow Links or not?
Analyze NoFollow Links or not?
From the findings above, it seems that reviewing the link risk of NoFollow links is still a must. Against different statements from Google, any link can potentially lead to a Penalty.
In order to respond to the different views regarding NoFollow links, Link Detox (DTOX) grants users the possibility to analyze or ignore NoFollow links while performing link audits. We always recommend analyzing NoFollow links, but we leave it up to you.
Do not miss the update from September 10, 2019 on the NoFollow 2.0 and new link attributes UGC and SPONSORED.
Learn all about NoFollow 2.0, UGC and SPONSORED Link Attributes
FAQ on NoFollow Links #
Can NoFollow Links cause a Google Penalty?
Yes, we’ve seen that happen. We also received spam examples from Google specifically pointing to NoFollow links.
How many SEOs believe NoFollow Links should be audited and taken care of?
In 2014 already 50% of webmasters and SEOs decided to take the risk of NoFollow Links serious. With the NoFollow 2.0 introduced in September 2019 we believe the number has gone way up. We also recommend everyone to audit NoFollow Links.
Can Link Detox/LinkResearchTools (LRT) perform link audits without NoFollow links?
Yes, the option to decide if NoFollow links are audited and calculated a potential link risk for exists since 2014. Users can perform the audit in two phases, first without NoFollow links, then with NoFollow links included.
Can nofollow links hurt your Google rankings?
Yes, we’ve seen that happen. We also received examples from Google specifically pointing to NoFollow links.
Do NoFollow links have value?
If you have NoFollow links on reputable and trusted sites, they certainly have value. Just think about links from Wikipedia. With the NoFollow 2.0 introduced in September 2019 we believe that the value of such links has increased even more.